An investigation on how to detect OOM processes
So I have been investigating some processes on a gunicorn based service running on AWS beanstalk. Here are some of my findings, on how to detect specifically processes killed by the linux OOM Killer.
I made use of the following tools:
- Stress-ng
Stress-ng will stress test a computer system in various selectable ways. It was designed to exercise various physical subsystems of a computer as well as the various operating system kernel interfaces.
- Perl Script
1
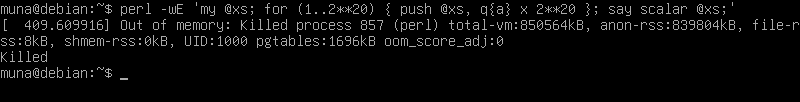
perl -wE 'my @xs; for (1..2**20) { push @xs, q{a} x 2**20 }; say scalar @xs;'
Initialization: my @xs; initializes an empty array @xs which will hold strings of 'a'’s.
Loop: for (1..2**20) { push @xs, q{a} x 2**20 }; iterates 2^20 (1,048,576) times. In each iteration, it constructs a string containing 2^20 (1,048,576) 'a' characters (q{a} x 2**20) and pushes this string onto the array @xs.
Output: say scalar @xs; prints the number of elements in the array @xs. Since the loop pushes one element into @xs in each iteration, scalar @xs will output 2^20, which is 1,048,576.
The entire command effectively generates and stores 1,048,576 strings of 'a’s in an array and then prints the total count of these strings.
- Dmesg
Dmesg (diagnostic messages) is a command on most Unix-like operating systems that prints the message buffer of the kernel. The output includes messages produced by the device drivers.
- Swapoff
Swapon, swapoff - enable/disable devices and files for paging and swapping.
A bit of background on the linux OOM Killer:
It is the job of the linux ‘oom killer’ to sacrifice one or more processes in order to free up memory for the system when all else fails. It will also kill any process sharing the same memory descriptor (mm_struct) as the selected process, for obvious reasons. Any particular process leader may be immunized against the oom killer if the value of its /proc/<pid>/oomadj is set to the constant OOM_DISABLE.
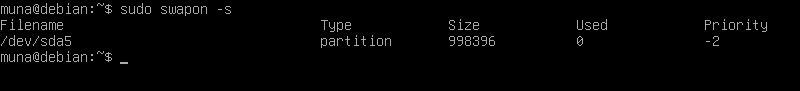
Since aws services don’t have swap , i have to disable swap. swapon -s tells you what swaps are currently enabled. sudo swapoff -a disables all swaps; sudo swapon -a is usually sufficient to reenable them.
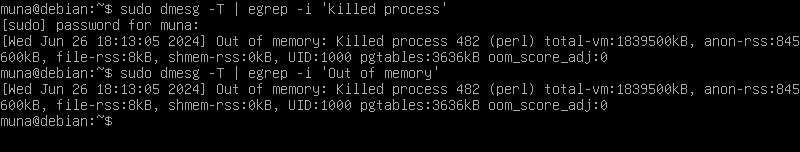
Running the perl script I showed above triggers the OOM killer. The logs for these can be found at /var/log/syslog or /var/log/messages. These logs can be accessed with
1
sudo dmesg -T | egrep -i 'killed process'
and
1
sudo dmesg -T | egrep -i 'Out of memory'
Below are some screenshots on the tests I ran on a debian virtual machine:
I will be trying to implement a cron job that checks dmesg regularly and logs the errors.